The project
Accelerated climate change and related weather extremes
In the last decade, an unprecedented acceleration in climate change and related extreme weather events has occurred. In 2022, Europe experienced the hottest summer on record with a severe drought and raging wildfires. Countries were struck by extreme floods with Pakistan being the worst-hit (33 million people affected).
The IPCC Summary for Policymakers (IPCC, 2021) notes “widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere and biosphere have occurred” and are “already affecting many weather and climate extremes in every region across the globe” due to human influence. Also, “continued global warming is projected to further intensify the global water cycle, including its variability, global monsoon precipitation and the severity of wet and dry events”.
The role of clouds on weather and climate
Clouds are key modulators of the Earth’s energy balance and any perturbation due to aerosol–cloud interactions (ACI) can profoundly impact weather and climate influencing both natural and human systems. ACI contributes ~3 times more than aerosol-radiation interactions (ARI) to the negative Effective Radiative Forcing (ERF) of aerosols on climate. Although it is virtually certain that aerosol forcing exerts a net cooling impact upon climate, partly masking greenhouse gas warming, its magnitude is highly uncertain and varies strongly with time and location, which severely limits our understanding of how global and regional climate respond to changes in GHGs.
There are major outstanding questions as to how aerosol–cloud interactions (ACI) and aerosol-radiation interactions (ARI) controls/modifies these climate extremes and extreme weather events, which requires improved predictive models and knowledge of processes controlling aerosols, clouds, and their interactions from hours to decades.
Key target ACI uncertainties
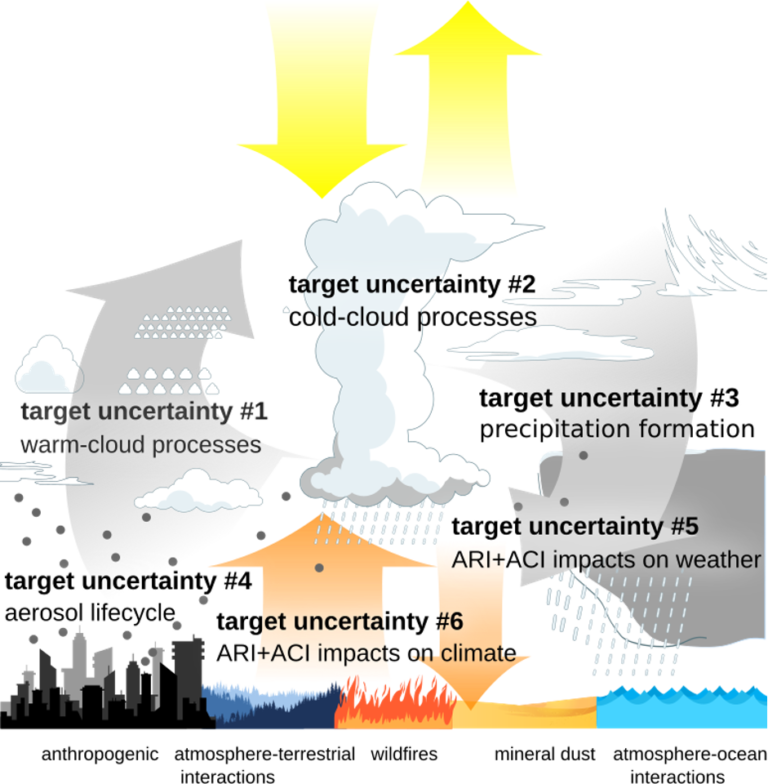
CERTAINTY aims to train the next generation of multidisciplinary, diverse ACI scientists. To improve our predictions of climate sensitivity and future climate response, CERTAINTY will organize interdisciplinary courses/workshops on topics relevant to achieve the goal of improving understanding and constraining the role of ACI/ARI.
CERTAINTY partners are leading the development for the retrieval algorithms of the next generation of satellites (EarthCARE, MetOp-SG). The project will be in key role in early adoption of the novel aerosol and cloud data provided by these satellite retrievals.
The data will further be linked to European data and modelling infrastructures improving ground and aircraft-based remote sensing methodologies, cloud scale models, numerical weather prediction models, and high resolution and Earth system models (ESMs).
CERTAINTY will use EU infrastructures to deliver FAIR and open science.